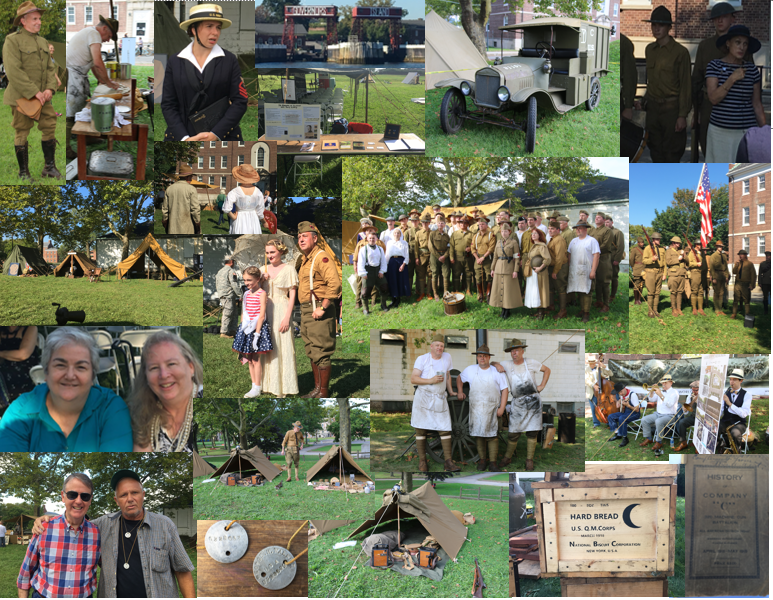
Review of “They Shall Not Grow Old”
This week I went to see the limited showing of Peter Jackson’s “They Shall Not Grow Old”. By now, you probably know that the film has been colorized, and dubbed, all with great technical care. But the movie is so much more than that. It is an experience. Mr. Jackson is an engaging story teller who has done phenomenal work in bringing this Great War footage to us differently than has ever been attempted. For him, it was a labor of love, dedicated especially to his Grandfather.
The story followed British soldiers from home to training, then the trenches and combat, and back home. The movie was a composite experience, using movie footage from the Imperial War Museum and audio from many BBC and IWM interviews of British soldiers. It captured the Western Front experience, including the sights and sounds of being in the trenches and a trench raid. The actual scenes of combat were depicted through the use of artwork from contemporary publication “The War Illustrated”. Although the movie was about British soldiers, the heart of the story was applicable to soldiers from all countries.
The movie was unflinching in showing the horror and devastation of the war. It equally showed the human side with the soldier’s everyday life and their interactions with German prisoners of war. There were horses and tanks, showing old and new ways of waging war meeting on the battlefield.
After the movie ended, most of the audience remained to spend some promised time with Mr. Jackson. His story telling ability also shined in his short feature after the movie’s credits where he shared how the story began and how it was made. The technology and techniques involved were fascinating. The people who worked on the project were professionals, and the parts that went into creating this experience were interesting.
Mr. Jackson’s dedication to the project and its content were unquestionable. He showed us his assortment of authentic uniforms. The archival research was terrific, highlighted by his finding the orders that were being read in a film clip. He even went to great lengths to get authentic sounds to accompany the footage. In this day of digital sounds, it was great to see a Foley artist at work. He also shared how many other stories were in the Imperial War Museum Archives, from different missions in the British Expeditionary Force to women working on the home front.
My fondest hope is that more WWI footage is restored using his approach and brought to the public. That would be a great way to keep this from being a “forgotten” war.
For me, his thoughts at the end were as compelling as his project itself. As a non-historian, he had made a movie for non-historians to motivate them to find out about their WWI ancestors. He encouraged people to find out these stories, because those stories are important to us. Through my books, lectures and participating in WWI Centennial events, this is what I have also tried to do in my own way.
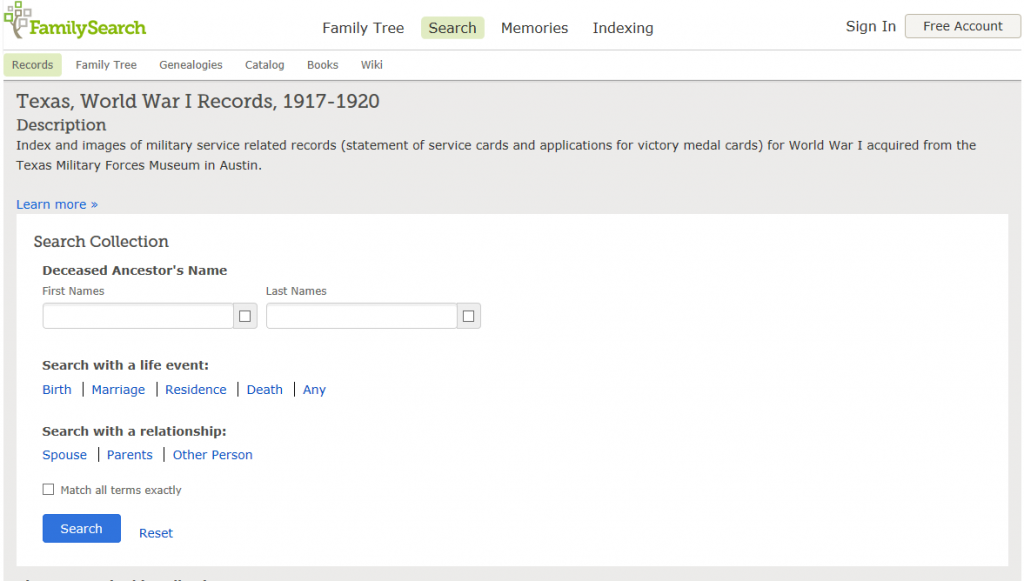
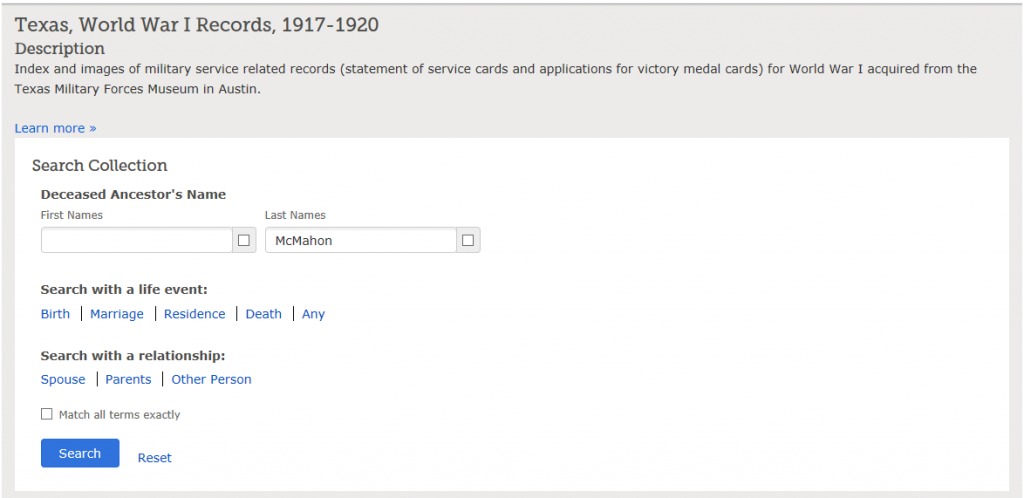
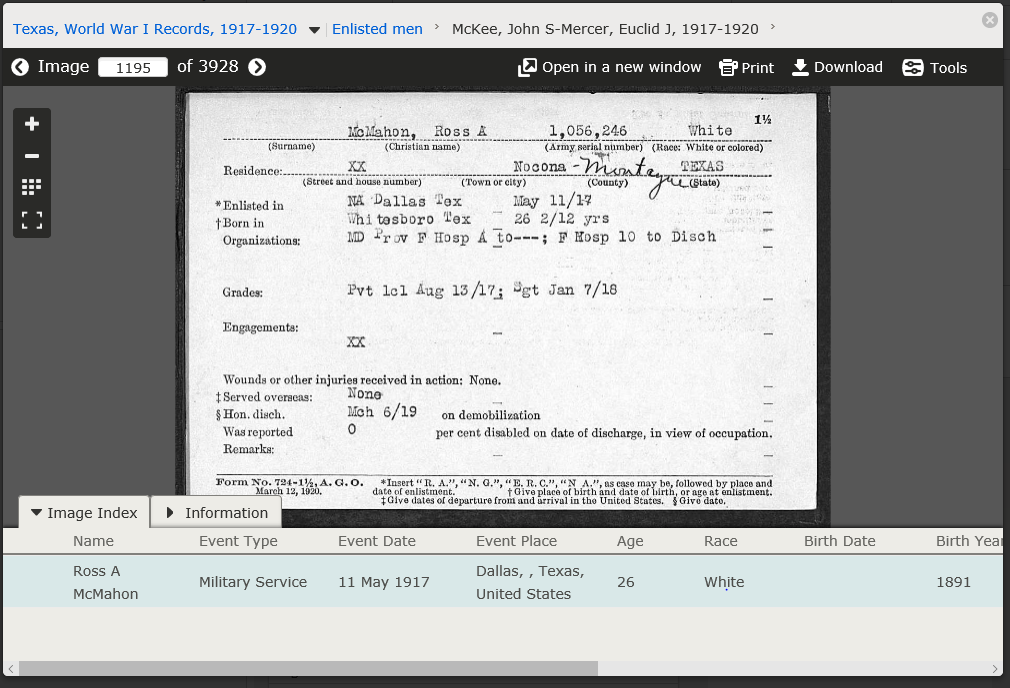
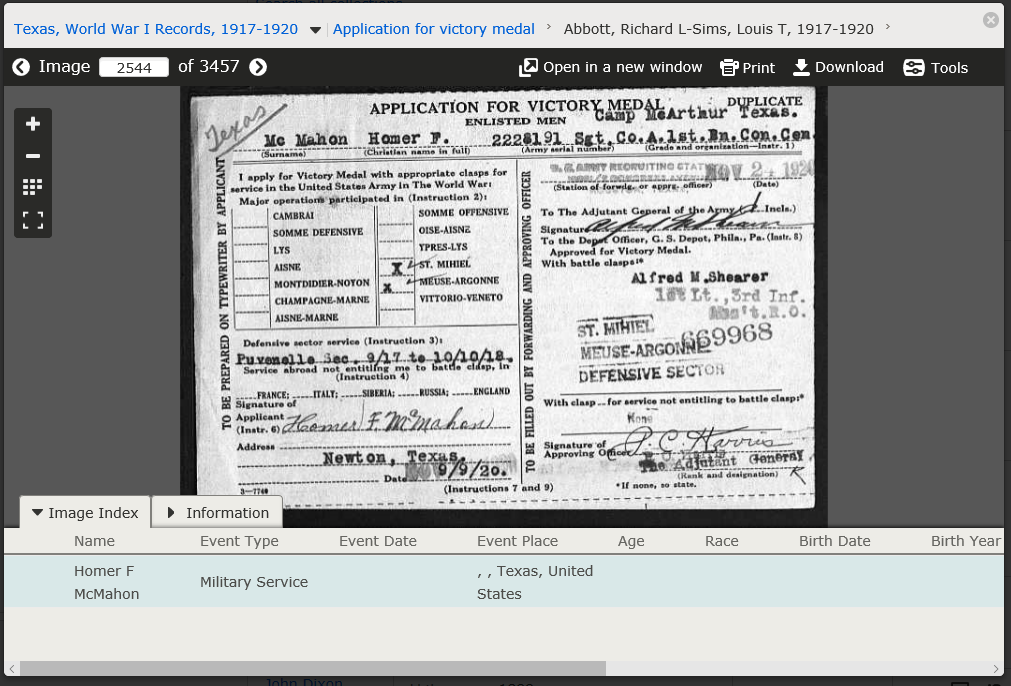
This review ends with homework: “Do you have any WWI ancestors?”