AI: Meta Prompting
If you have attended one of my AI presentations, then you know how important it is to develop prompt engineering skills to get the most out of Large Language Models (LLMs). The good news is that we do not always have to create the perfect prompt on our own!
There is a harsh term used in my field, GIGO, which stands for Garbage In, Garbage Out. When it comes to AIs, this applies to the fact that the LLM response (output) will only be as good as our prompts (input).
A simple explanation of meta prompting is to have one Large Language Model (LLM) create a prompt for another one. Meta prompting is more involved than that because it builds a prompt with more specific instructions about the steps to take to realize the goal of the prompt. It is as if the LLM is translating what you want to do into LLM language!
The cinematic arts student at my home gave me some insights into his practical use of meta prompting. He was having an issue with an AI that generates video. It was not creating what he was describing, so he turned to ChatGPT to explain his vision and ask for a prompt to use for generating that image. ChatGPT dutifully responded with a prompt that did work with the AI video generator. The message is that when it comes to crafting prompts, we are not on our own.
While working to understand meta prompting, I thought of an example application to try before applying this skill to genealogy. I asked ChatGPT to create a prompt for me that I could use to have a research report generated for me about a topic. I also specified what and how I wanted to investigate the topic, as well as the fact that I wanted sources and in-text citations. Using the power of the AI to recognize patterns, I certainly wanted analysis to be part of generating the data in the report.

A prompt was created, but ChatGPT had some specific questions that it included in its response about the type of citation I wanted and asked if there were other constraints, such as word count or including quotes. We had a conversation to refine the prompt, starting with a 308-word prompt and concluding with the final response which was a modular, reusable 1122-word prompt.
The prompt began with: “You are an expert in …
The prompt contained sections for FOCUS & SCOPE, RESEARCH & SOURCES, STRUCTURE OF THE REPORT, STYLE & LENGTH and FINAL OUTPUT
ChatGPT’s prompt also included some interesting anti-hallucination guidance: “If there are areas where evidence is limited (for instance, few direct author comments about a particular name), clearly indicate uncertainty and base comments on reasonable inference, not fabrication.”
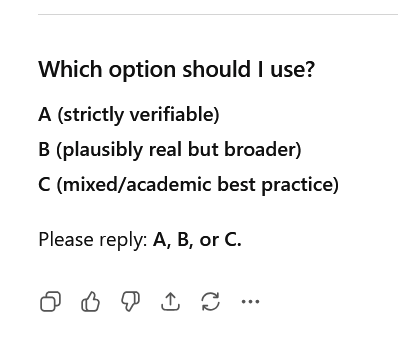
I decided to use the prompt in ChatGPT, and opened a new chat. I pasted in the prompt, and it responded with a request for clarification:

It offered me options, providing details, which are omitted for brevity:
- Option A — Use only 100% verifiable, well-known, widely documented sources
- Option B — Allow me to cite plausible but harder-to-verify sources
- Option C — A blended approach
Then it asked me to respond with which option it should use:
After the clarification interaction, ChatGPT told me that

It waited for my response before it began to generate the report:

The report was reasonable, and described patterns. ChatGPT offered me formats for downloading the report and other products based on the report, an executive summary and PowerPoint presentations. If I want to dig deeper, this report is valuable to me as a starting place.
Of course, the caveats still remain about not using this for school reports (unless the assignment calls for the use of AI) and not submitting it to a client. There can be tell-tale signs of an AI-generated report, as I know from a high school science fair project done by that same cinematic arts student, and documentation out on the web.
So, will you try meta prompting? Let me know how you do.



